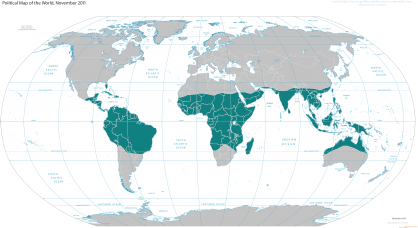
Tropical zone
Characteristics
- Area
- Around the equator, from 23.5° further north to 23.5° southern latitude
- Sun path
- Sun at the zenith (90°) at least once per year, never lower than 43°
- Average temperature
- >20 to 30°C
- Minimal temperature
- 0°C (no frost)
- Maximal temperature
- Up to 40°C (seldom more)
- Radiation
- Positive
- Daylength
- 10 to 13.5 hours
- Precipitation
- Rain - will be defined by trade winds and its seasonal shift
- Climate
- Humid - warm. Often precipitation (humid), sometimes (short) drought. "Day time" instead of "season climate" (daily changes in tempperature are bigger than the annual changes of daily averages).
- Vegetation
- Evergreen forests, savannah
- Properties
- More than 40% of Earth's population live in the tropics, with an increasing tendency
Subdivisons of the tropical zone
Within the Tropics there are different vegetation zones. These depend on the time during which there is sufficient water available for plants to grow. The differentiation is made according to the number of dry (arid) and wet (humid) months:
- humid: 12 to 9½ humid months = tropical rainforest,
- semi-humid: 9 ½ to 7 humid months = wet savannah,
- semi-humid: 7 to 4½ humid months = dry savannah,
- semi-arid: 4 1/2 to 2 humid months = thorn savannah and
- arid: 2 to 0 humid months = desert.
Close to the equator, the humid climate changes to a semi-humid resp. semi-arid tropical
climate towards the Tropics, which results in different ecozones, from tropical forests over various types of
savannah to the tropical semi-deserts and deserts.
In the humid tropics, which surround the equator with
exception of East Africa and the Andes, tropical rain forests form. The semi-humid tropics, in which the dry and wet
seasons shape the seasons, are characterised by savannah, dry forests
and monsoon forests, which frame the tropical rain forests. Wetlands of the Pantanal in South America also belong to
this zone. The arid tropics are deserts and semi-deserts, where only small changes of temperature occur in the
course of the year.
Tropical zone: further description
The tropical zone (tropai heliou Sun turning areas) is the warmest climate zone of the Earth. The tropics are:
- areas of "climate radiation", which are limited by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn (23,5° northern and southern latitude) and in which the Sun stands at least once the year at the zenith (highest conditions = 90°C to the ground);
- in the system of the atmospheric circulation, the range between the two edges between subtropical and tropical high pressure belts of the northern and southern hemispheres of the Earth;
- the zones on both sides of the equator that are shaped by higher daily temporal (time of day climate) and smaller seasonal variations in temperature (25 °C annual averages); due to that, there is a high irradiation all year around and no thermal seasons can form;
- the range within which the daily lengths in the course of the year vary only slightly between 10,5 and 13,5 hours.