Land-sea wind
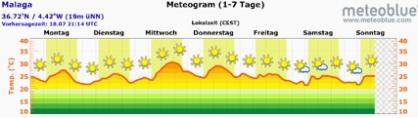
During the day, the sunshine radiation heats the land surface more than the ocean, which one has a bigger thermal mass. Therefore, the warm air rises above the land and colder air flows from ocean to land. At night, this process inverts (see meteograms for Malaga). Now, the land cools down while the ocean surface keeps its temperature. The air rises above the ocean, and cold air flows from the land to the ocean. This kind of land-sea winds are well-known on every coast.

Example of northern Germany

Germany lies on the Northern Hemisphere of the Earth in the temperate zone, where different seasons occur. The land-sea winds are most visible during the summer, when the Sun reaches its highest position: then the temperature differences between land and sea are higher. The location of the selected coastal region is shown in the accompanying figure.
On land (20 km from coast)
On the coast
On sea (20 km from coast)
Example of Italy
Italy is also located on the Northern Hemisphere of the Earth in the temperate zone. The land-sea wind here is also most visible during the summer. The location of the selected coastal region is shown in the accompanying figure.
On land (20 km from coast)
On the coast
On sea (20 km from coast)
Questions
- Can you recognise whether a land-sea or sea-land wind is blowing at the coast?
- If not, could it be that the temperatures do not differ between day and night?
- Is the wind influenced by other factors, such as cold winter or by dense cloudy cover?
- Do the wind direction and the wind force change in 20 km distance from the coast?


